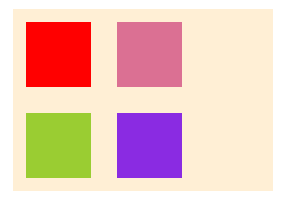
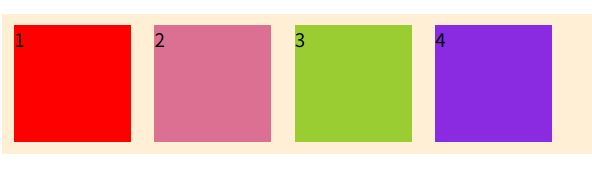弹性布局
flex布局是css3中的新布局模块,为盒模型提供了最大的灵活性,可以改进容器中的项目对齐,方向和顺序,flex可以自动调节子元素的高度或者宽度
六个主要属性
flex-direction
决定主轴方向
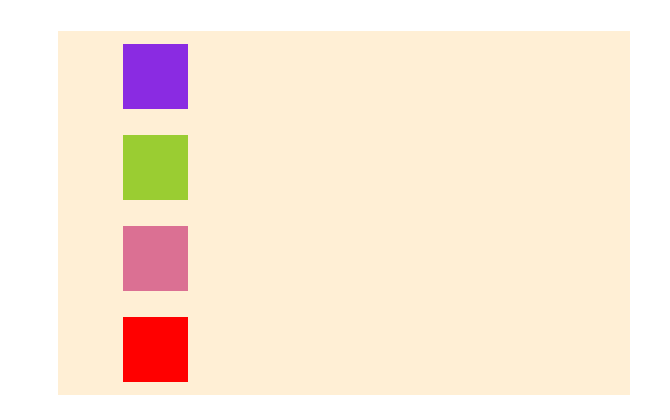
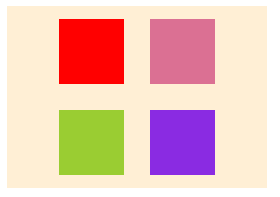
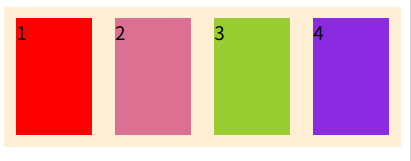
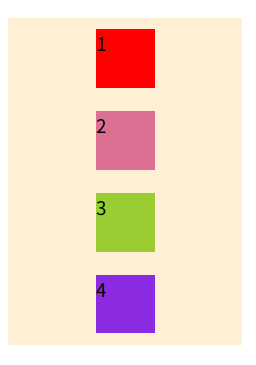
row:水平方向 左 --> 右- row-reverse:水平方向 左 <-- 右
- column:垂直方向 上 --> 下
- column-reverse:垂直方向 上 <-- 下
示例
html
<ul id='father'>
<li class='child1 child'></li>
<li class='child2 child'></li>
<li class='child3 child'></li>
<li class='child4 child'></li>
</ul>css
#father {
display: flex;
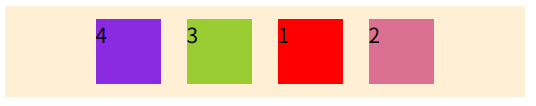
flex-direction: row;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 100px;
transform: translateX(-50%);
width: 400px;
background-color: papayawhip;
}
.child {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
margin: 10px;
display: block;
}
.child1{
background-color: red;
}
.child2{
background-color: palevioletred;
}
.child3{
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
.child4{
background-color: blueviolet;
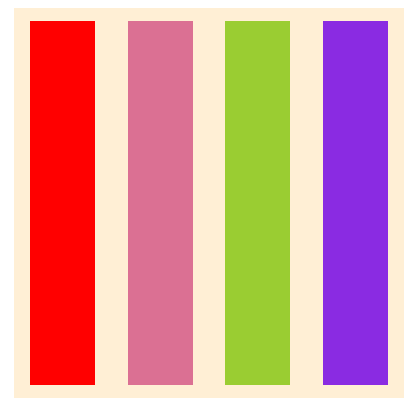
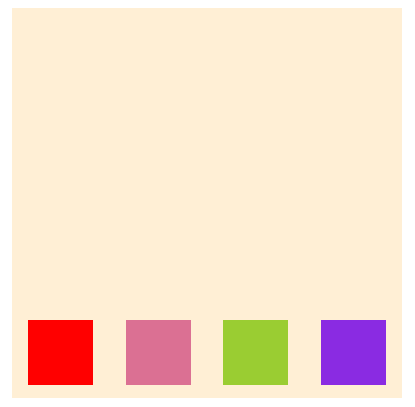
}- row
- row-reverse
- column
- column-reverse
flex-wrap
设置子元素的换行方式
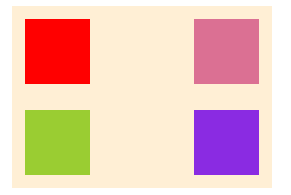
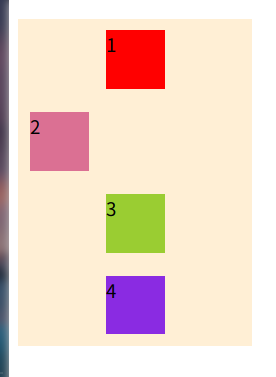
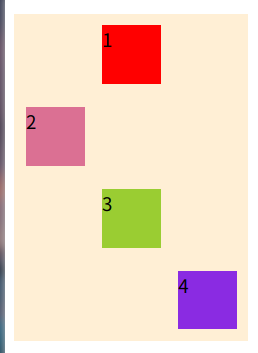
nowrap:不换行- wrap:换行 上 --> 下 第一行在上方
- wrap-reverse 上 <-- 下 第一行在下方
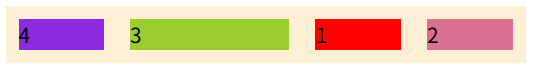
接着上面的示例更改一下父容器的属性,下面的示例 flex-direction属性为row
css
#father {
/* 改动的属性 */
width: 150px;
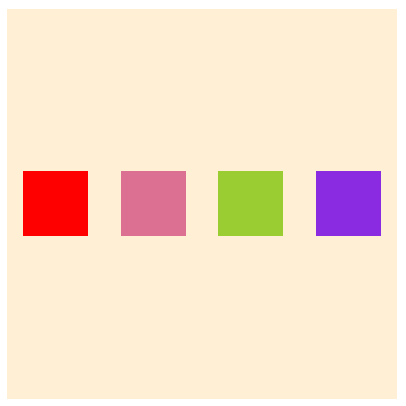
}- nowrap
- wrap
- wrap-reverse
flex-flow
其为 flex-direction 与flex-wrap的简写
css
flex-flow:flex-direction flex-wrap用上面的例子
css
#father{
flex-direction:row-reverse;
flex-wrap:nowrap;
}等价于
css
#father{
flex-flow:row-reverse nowrap;
}justify-content
设置子元素在父容器主轴上的对齐方式
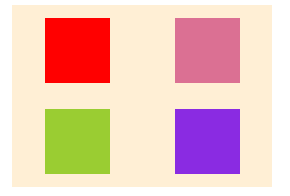
flex-start:左对齐- flex-end:右对齐
- center:居中
- space-between:两端对齐:每个子元素之间的间隔一致
- space-around:每个子元素两侧间隔一致
继续改动父元素的部分样式做实验
css
#father {
width: 200px;
flex-flow: row wrap;
justify-content:flex-start;
padding:0;
}flex-start
- flex-end
- center
- space-between
- space-around
align-items
子元素在交叉轴上的对齐方式
- flex-start:交叉轴起点
- flex-end:交叉轴终点
- center:交叉轴中点
- baseline:以子项目的第一行文字为基线对齐
stretch:未设置高度,将占满整个容器高度
css
#father {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
padding: 0;
flex-flow: row wrap;
justify-content: space-around;
align-items: flex-start;
}- flex-start
- flex-end
- center
- baseline
css
#father{
flex-flow: row wrap;
justify-content: center;
width: 600px;
padding: 0;
align-items: baseline;
}html
<ul id='father'>
<li class='child1 child' style="padding: 10px;">1<br>666</li>
<li class='child2 child' style="padding: 30px;">2<br>666</li>
<li class='child3 child' style="padding: 50px;">3<br>666</li>
<li class='child4 child' style="padding: 70px;">4<br>666</li>
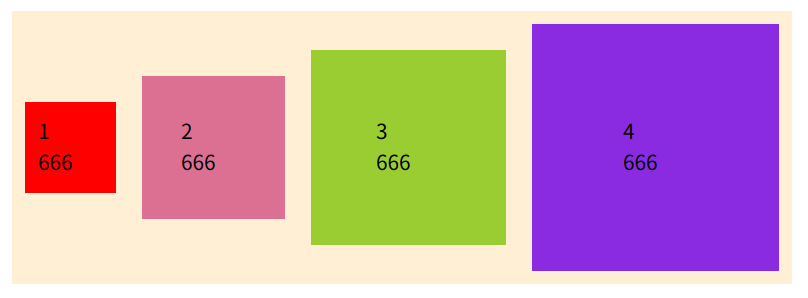
</ul>- stretch
去掉子元素的height属性
css
.child{
/* height:50px */
}align-content
多行情况下的对齐方式,类似justify-content的对齐方式
- flex-start:交叉轴起点
- flex-end:交叉轴终点
- center:交叉轴中点
- space-between:交叉轴两端对齐
- space-around:每行之间上下间隔一致
stretch:占满整个空间,下方留一些空白
六个项目属性
测试用例
css
#father {
display: flex;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 100px;
transform: translateX(-50%);
background-color: #ffefd5;
width: 400px;
flex-flow: row wrap;
justify-content: center;
padding: 0;
}
.child {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
margin: 10px;
display: block;
}
.child1{
background-color: red;
}
.child2{
background-color: palevioletred;
}
.child3{
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
.child4{
background-color: blueviolet;
}html
<ul id='father'>
<li class='child1 child'>1</li>
<li class='child2 child'>2</li>
<li class='child3 child'>3</li>
<li class='child4 child'>4</li>
</ul>order
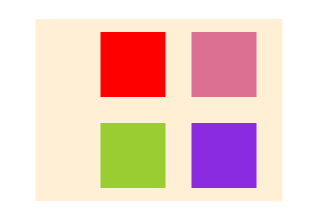
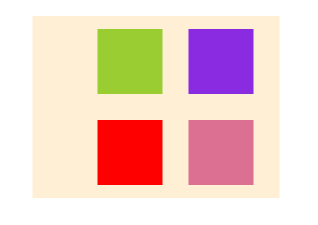
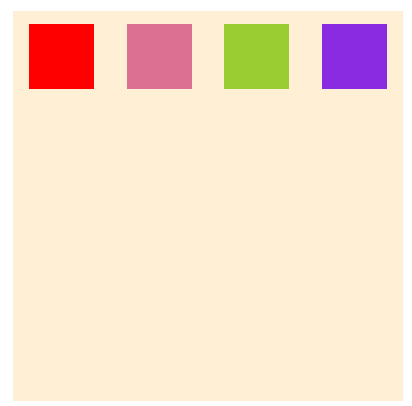
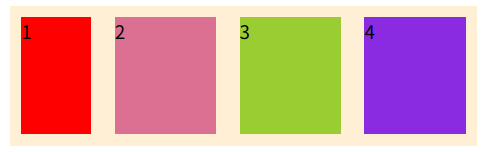
规定子元素的排列顺序,数值越小越靠前,默认0
为child3,child4加上order
css
.child3 {
order: -1;
}
.child4 {
order: -2;
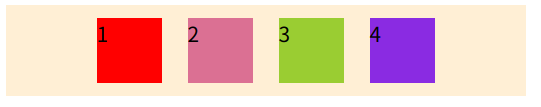
}加之前
加之后
flex-grow
子元素放大比例,剩余空间不足则不会放大,默认0
注释掉子元素的宽高
css
.child {
/* width: 50px; */
/* height: 50px; */
margin: 10px;
display: block;
flex-grow:1
}改动第三个
css
.child3 {
flex-grow:2
}块3就是其它块的两倍宽度
flex-shrink
规定子元素的缩小比例,默认1,空间不足则会缩小
修改部分样式
css
#father {
flex-flow: row nowrap;
}
.child {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.child1{
flex-shrink:3;
}flex-basis
修改子元素占据主轴空间的大小,默认auto为子元素的实际宽度
测试用例
css
#father {
display: flex;
background-color: #ffefd5;
flex-flow: row nowrap;
padding: 0;
}
.child {
height: 100px;
margin: 10px;
display: block;
flex-basis: auto;
}
.child1 {
background-color: red;
}
.child2 {
background-color: palevioletred;
}
.child3 {
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
.child4 {
background-color: blueviolet;
}html
<ul id='father'>
<li class='child1 child'>1</li>
<li class='child2 child'>2</li>
<li class='child3 child'>3</li>
<li class='child4 child'>4</li>
</ul>设置flex-basis为100px时
css
.child{
flex-basis:100px
}空间充足
空间不足
即当不设置width宽度时就以设置的flex-basis属性作为子元素在主轴上的宽度
flex
flex是flex-grow,flex-shrink,flex-basis的缩写,默认0 1 auto,后两个属性可选
css
flex:flex-grow flex-shrink flex-basisalign-self
允许单个子元素与其它子元素有不同的对齐方式,可覆盖align-items属性 默认值auto
示例
html
<ul id='father'>
<li class='child1 child'>1</li>
<li class='child2 child'>2</li>
<li class='child3 child'>3</li>
<li class='child4 child'>4</li>
</ul>css
#father {
display: flex;
width: 200px;
background-color: #ffefd5;
flex-flow: column nowrap;
padding: 0;
align-items: center;
}
.child {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
margin: 10px;
display: block;
}
.child1 {
background-color: red;
}
.child2 {
background-color: palevioletred;
}
.child3 {
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
.child4 {
background-color: blueviolet;
}让第二个左对齐
css
.child2{
align-self: flex-start;
}接着让第四个右对齐
css
.child4{
align-self:flex-end;
}